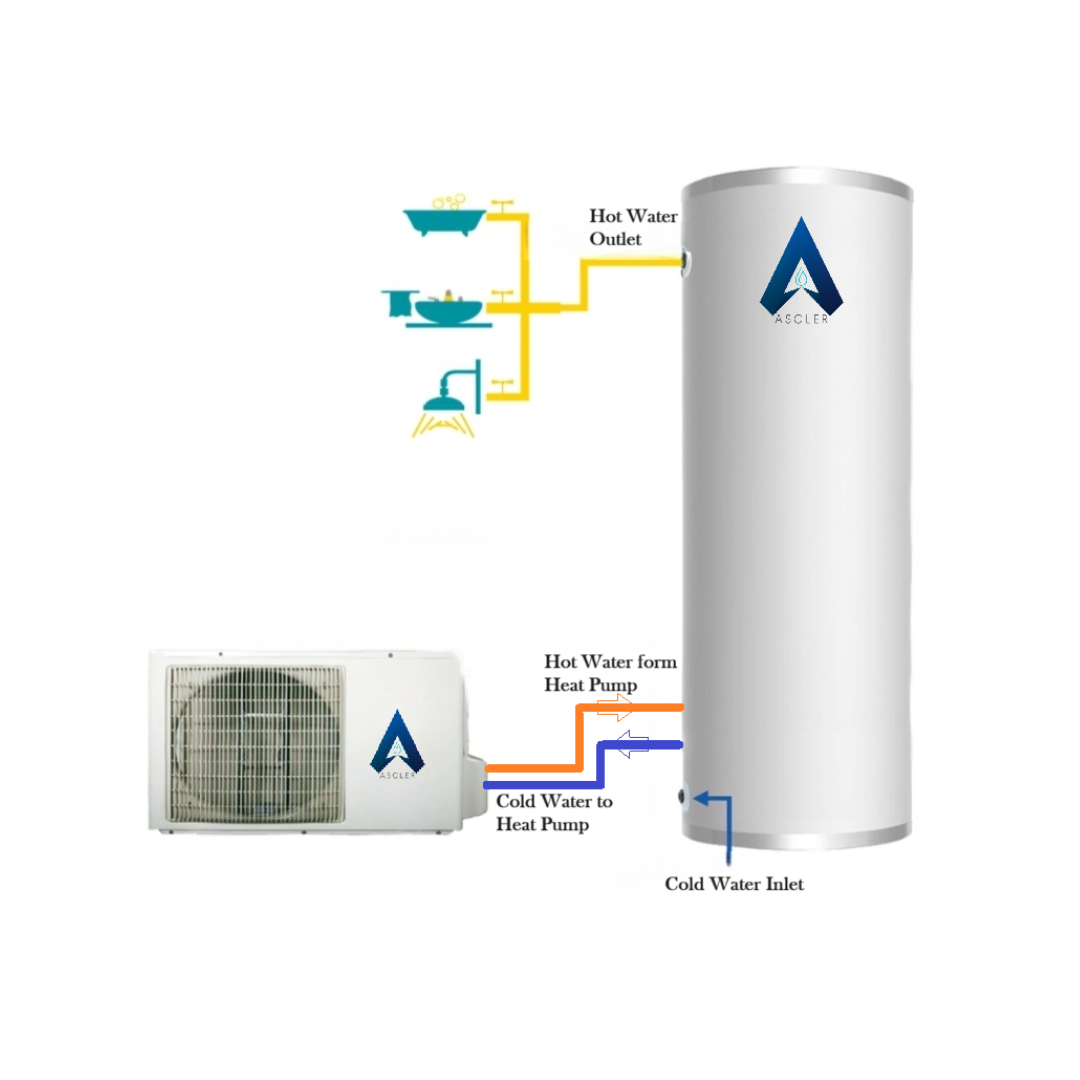
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat energy from a source of heat to what is called a heat sink. Heat pumps move thermal energy in the opposite direction of spontaneous heat transfer, by absorbing heat from a ambient air and releasing it to a warmer one.
A heat pump uses a very small amount of external power to accomplish the work of transferring energy from the heat source to the heat sink. The most common design of a heat pump involves four main components – a condenser, an expansion valve, an evaporator and a compressor. The heat transfer medium circulated through these components is called refrigerant.
Compression and expansion of a working fluid-commonly known as ‘refrigerant fluids pass through the Heat Pump’s four main components: evaporator, compressor, condenser and expansion device.
Air source heat pumps (ASHP) is a process that by using the principle of vapor compression, transfers the hot air from a place to another exactly in the same way as the system of a refrigerator does. Before looking at the details of the technology, it is important to note that air at a temperature above absolute zero always contains some heat and many of these pumps manage to extract heat even at low temperatures as -15 C degrees. The pump consists of two exchanger coils: one outside that catches the hot air and an internal one that pushes the air through a heating system.
The Technology in a Nutshell : Air source heat pumps systems consist of four major elements that allow the refrigerant to pass from the liquid state to the gas: a compressor, a condenser, an expansion valve and an evaporator. When the refrigerant passes through the heating system, the high temperature (usually 100 degrees or more) transforms it into vapor or gas while the energy produces heat. The gas then goes through the compressor that increases its temperature, and then through the expansion valve that makes the hot air enter the building. Next the hot air passes in a condenser that turns the gas into liquid again.
The heat produced by the energy in the evaporation phase passes through the heat exchanger again to restart the cycle and it is used to make the radiators work, for domestic, swimming pool, commercial & industrial hot water.
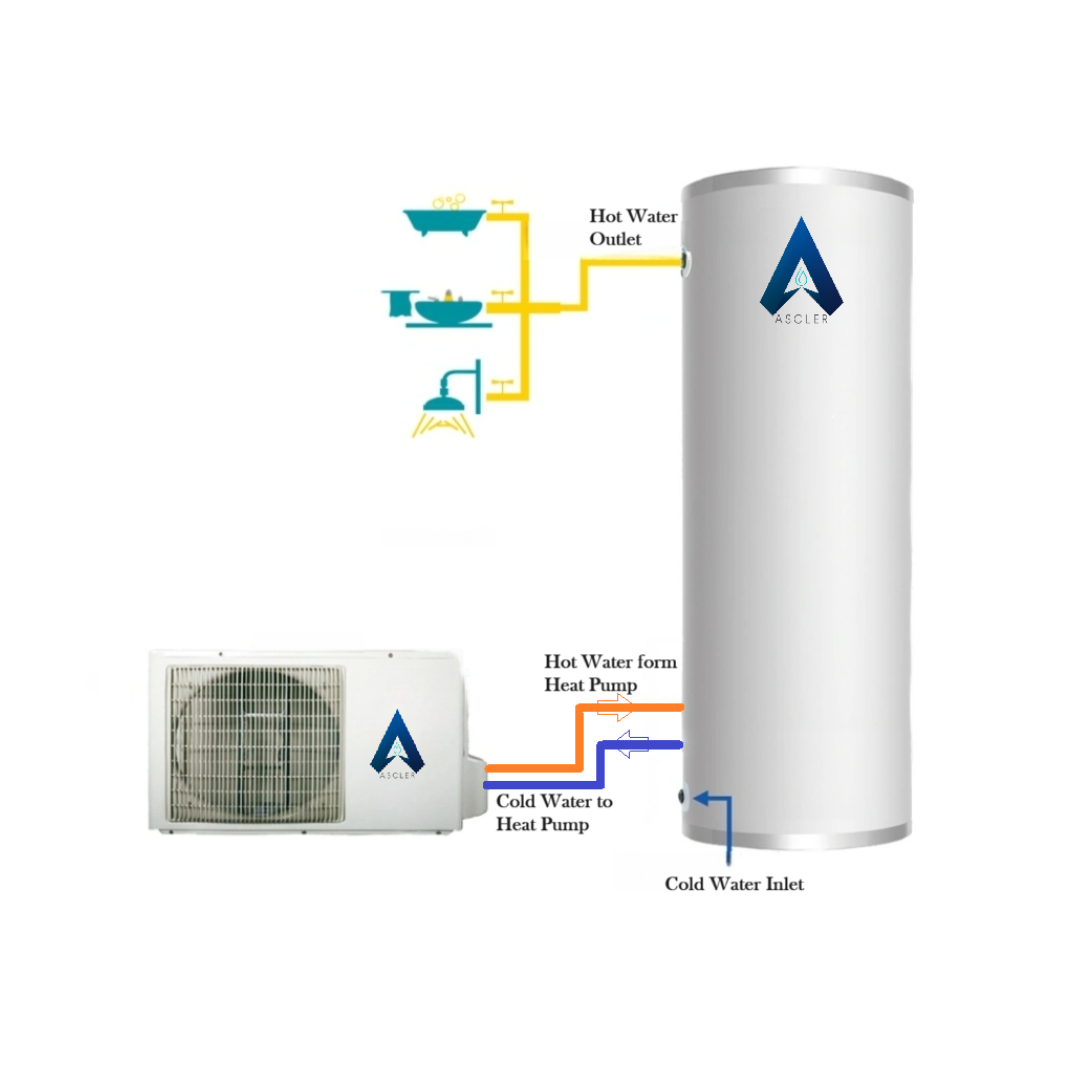
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat energy from a source of heat to what is called a heat sink. Heat pumps move thermal energy in the opposite direction of spontaneous heat transfer, by absorbing heat from a ambient air and releasing it to a warmer one.
A heat pump uses a very small amount of external power to accomplish the work of transferring energy from the heat source to the heat sink. The most common design of a heat pump involves four main components – a condenser, an expansion valve, an evaporator and a compressor. The heat transfer medium circulated through these components is called refrigerant.
Compression and expansion of a working fluid-commonly known as ‘refrigerant fluids pass through the Heat Pump’s four main components: evaporator, compressor, condenser and expansion device.
Air source heat pumps (ASHP) is a process that by using the principle of vapor compression, transfers the hot air from a place to another exactly in the same way as the system of a refrigerator does. Before looking at the details of the technology, it is important to note that air at a temperature above absolute zero always contains some heat and many of these pumps manage to extract heat even at low temperatures as -15 C degrees. The pump consists of two exchanger coils: one outside that catches the hot air and an internal one that pushes the air through a heating system.
The Technology in a Nutshell : Air source heat pumps systems consist of four major elements that allow the refrigerant to pass from the liquid state to the gas: a compressor, a condenser, an expansion valve and an evaporator. When the refrigerant passes through the heating system, the high temperature (usually 100 degrees or more) transforms it into vapor or gas while the energy produces heat. The gas then goes through the compressor that increases its temperature, and then through the expansion valve that makes the hot air enter the building. Next the hot air passes in a condenser that turns the gas into liquid again.
The heat produced by the energy in the evaporation phase passes through the heat exchanger again to restart the cycle and it is used to make the radiators work, for domestic, swimming pool, commercial & industrial hot water.
For inquiries or assistance, contact Ascler today. Our team is ready to provide expert advice and support for all your heating and cooling needs.
For inquiries or assistance, contact Ascler today. Our team is ready to provide expert advice and support for all your heating and cooling needs.

Copyright © 2024 Ascler. All rights reserved.
For inquiries or assistance, contact Ascler today. Our team is ready to provide expert advice and support for all your heating and cooling needs.
Copyright © 2024 Ascler. All rights reserved.
